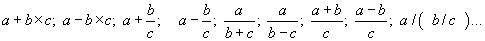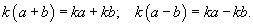|
 |
Name
MA²ThE-TE-AMO
MAking MAThEmatics TEAchers MObile
Code
129543-CP-1-2006-1 -IT-COMENIUS-C21
Action/type
COMENIUS-C21
Project span
01.10.2006
01.10.2009 |
|
 |
 |
| |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
French participating school and Mathematics topics
Collège du Parc«Collège
du parc» is a lower secondary school in Sucy en Brie.
Sucy en Brie is a town
in the subdivision 94 (Val-de-Marne) nearby Créteil, with 25000 inhabitants.
Main of these inhabitants is in upper or middle class.
Webpage : http://www.ac-creteil.fr/clgduparcsucy/
610 pupils
| division |
Number of pupils |
| 6ème (11 years old) |
147 |
| 5ème (12 years old) |
166 |
| 4ème (13 years old) |
144 |
| 3ème (14 years old) |
153 |
One class with
rugby option since year of “5ème”.
| Subjects |
Number of teachers |
| Music |
2 |
| Biology |
3 |
| English |
5 |
| Fine arts |
1 |
| French and Latin and Ancient Greek |
9 |
| German |
1 |
| History and geography and civics |
5 |
| Mathematics |
6 |
| Physics |
2 |
| Spanish |
2 |
| Sportive education |
6 |
| Technology |
3 |
There
are also 1 documentalist and 7 education assistants.
At the end of year of “3ème”84,5% of pupils succeed school
leaving certificate: general exam taken at fifteen (GCSE).
75% of pupils move
up to “lycée” , fifth form.
18% of pupils move up to vocational school.
4%
of pupils repeat their year.
3% of pupils go to apprenticeship (CFA).
Mathematical topics
in the
period September - November 2008
5ème (12 years old)Chapter 1: Numerical works
- Knowledge and use of the following words: sum, difference, product,
quotient, terms, factors, numerator and denominator.
- Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of two decimal numbers.
- Order of size of a result.
- Knowledge and use of operating priorities in numerical examples like:
- Knowledge and use of operation properties.
- To state and use distributive law in order to develop or factorize numerical
expressions:
- Solving a problem by writing and calculating an expression.
Chapter 2:
Point symmetry (rotation of 180° about the point)
- Definition of a symmetrical point to another point.
- Construction of a symmetrical point to another point.
- Construction of usual geometrical figures by point symmetry (straight line,
segment, circle...).
- Statement and use of point symmetry properties.
- To recognize the symmetry centre of a geometrical figure and to construct
centre.
- To complete a geometrical figure in order to get a symmetry centre.
Chapter 3: Algebraic expressions
- Reduction of a multiplication; for instance: a×3 = 3a.
- Knowledge and use of operating properties in algebraic expressions.
- Knowledge and use of distributive law in order to develop or factorize
algebraic expressions.
- Use of algebraic expressions to make numerical calculus.
- Equality test between two algebraic expressions by using numbers.
- Solving equations like: x+a=b and
x-a=b.
Chapter 4:
Angles, Parallelogram
- Knowledge and use of the expressions: adjacent angles, complementary angles,
supplementary angles, vertically opposite angles, alternate and interior angles,
corresponding angles.
- Statement and use of properties of angles made by two parallel lines which
are cut by a secant.
- Prove that two lines are parallel by using equality between alternate and
interior angles or corresponding angles.
- Showing equal angles in a figure and justifying.
- Connection of symmetry point properties to parallelogram.
- Statement and use of properties of a parallelogram.
- Construction of a parallelogram telling which properties are used.
- To prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Textbooks
 Click here to see the French
textbook excerpts on Fractions. Click here to see the French
textbook excerpts on Fractions.
 Click here to see the French
textbook excerpts on Pythagora's Theorem. Click here to see the French
textbook excerpts on Pythagora's Theorem.
| |
 |
 |
| |
|
|